How To Become A Doctor In Canada?

A doctor is a trained medical professional qualified to treat people who are suffering from medical disease or condition and have a highly privileged role. Working as a doctor is incredibly rewarding since you have the opportunity to improve society by assisting people in living healthier and happier lives. When you decide to become a doctor in Canada, you will have to make many decisions. There are many steps you will have to take. Canada is known as a health care superpower and as a country that values its citizens. It is important to remember that medical doctors are very respected, and a physician in Canada is considered a very professional and reliable individual. Therefore, becoming a doctor in Canada is one of the most sought-after career options for students and parents.
Canada is a great country for anyone looking to become a doctor. You can enjoy the great outdoors and high quality of living. It is a country that has everything you could want out of life. Some of its best features are the lower cost of living, a high standard of living, and the atmosphere of the country itself. Canada has many doctors and is always on the lookout for more.
One of the most exciting careers in medicine is that of a physician. However, the process is not simple and involves numerous steps that must be followed, and you need to go through a lengthy process. Look no further for information on how to become a doctor in Canada. Today, in this blog, we will walk you through the entire process, explain the two main paths to becoming a physician, and try to highlight the major differences between the two paths.
Pathways To Become A Doctor In Canada?
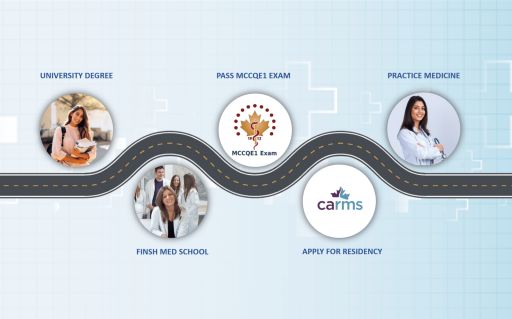
In Canada, there are two primary pathways to becoming a doctor/ physician. One is the well-known path which is a common path, and the other one is an alternative path. Let’s start with the common pathway; in this pathway, a Canadian citizen does not leave the country and continue her/his education, enter medical school. Graduate medical school, pass the MCCQE1 exam and continue her/his postgraduate education, complete residency program, and start practicing medicine in Canada after graduation as a medical specialist.
An alternative pathway includes two groups of a physician, those Canadian citizens who leave Canada to study medicine in foreign medical University and return to Canada after graduation to practice medicine in Canada and those who hold Canadian citizenship and are either graduating from medical school or are well-experienced specialists who would like to come to Canada and continue their medical practice here in Canada.
The Common Path To Become A Doctor In Canada:
The common pathway of becoming a Canadian doctor is not long; infect is straightforward, and it does not require you to pass the NAC exam. However, the process involves several steps that must be followed, such as finishing medical school and passing the MCQQE1 exam. Here is a closer look at the common pathway.
1- Get A University Degree
Before you embark on your journey to become a doctor in Canada, you must obtain a university degree. As per the rules created by the Medical Council of Canada (MCC), it should be a bachelor’s degree, at the minimum. However, the majority of medical schools will prefer your degree to be in the subjects of science. It might not always be mandatory to have a bachelor of science (BS) degree, but it will always be beneficial to you as it will help you understand the contents of the medical school curriculum in a better way. It might be challenging for those without a basic understanding of biology and chemistry concepts. All medical schools will also have a list of courses to be completed before you apply. These courses will mostly be in the field of science, so make sure you attend these during your degree studies.
2- Admission To A Medical School
Firstly, you will have to select the school you want to go to, out of the 17 medical schools registered under Canada’s Medical Council. Most of these schools require you to be a resident of the same province to study there. So before making any decision, you should perform a self-assessment of the requirements of each of the schools. You should contact the schools to understand the specific needs of the school. Passing the MCAT (Medical College Admission Test) is a requirement for most medical schools in Canada, so you should be prepared for that before applying to medical school. Canadian medical schools have standardized online application systems, which makes the process very easy now.
Canadian medical schools’ acceptance rate is very low at about 25%, so your credentials need to be fairly above average strength. A high university grade point average (GPA) is very crucial to guarantee acceptance. The duration of medical school is four years. The first two years are majorly about theoretic aspects leaning heavily on classroom and laboratory classes. The remaining two years include practical teaching in clinics where you watch and learn the treatment and clinical decision-making under a licensed doctor’s supervision.
3- Pass The MCCQE1 Exams
One of the requirements of becoming a licensed medical professional in Canada you need to pass the Medical Council of Canada Qualifying Examination (MCCQE) Part 1 exam. This exam is to assess your medical knowledge, competency, and clinical decision-making skills before you are allowed to work as an independent doctor in Canada.
The MCCQE part 1 exam is a crucial step on the road to becoming a medical doctor. However, when it comes to the MCCQE1 exam, many found it very challenging. They find the Medical Council of Canada (MCC) objectives so broad, and they don’t know where to begin. Many people have difficulty with the MCCQE1 exam, but it is not a difficult test to pass. The most important thing is to properly prepare for the test by studying all of the MCC objectives and practicing with high yield questions and clinical cases from a question bank.
Candidates who will take the MCCQE1 exam should have a thorough understanding of the MCCQE1 objectives because the exam is designed based on the MCC objectives. They will be tested on those objectives from all angles.
Understanding the MCCQE1 exam is the main key to success. It is a computer-based timed multiple-choice exam, which means that you need a combination of test-taking strategies, mainly time management, and a good study plan to help you to through the MCC objectives. The MCCQE1 exam can be challenging for those who are not well-prepared and unfamiliar with the exam format. To avoid this, practice with a question bank with questions that are as close as possible to those they will encounter on the actual exam and get familiar with the MCCQE1 exam format.
The main reason people fail the MCCQE1 exam is often due to a lack of a good study plan or underestimating the test-taking strategy that includes practicing questions and answering them correctly in under a minute. Without a study strategy, passing this exam will be difficult no matter how many hours you spend studying.
Most of the students start preparing for this exam during their medical school days as it takes a long time to cover the vast objective and practice to pass this exam. You can use notes and Question Bank available online to study for it.
It sounds overwhelming, but the good news is that Ace Qbank is designed based on the MCC Objectives and is regularly evolving, updating upcoming changes; it adequately covers both essential parts of the MCCQE1 exam. In addition, self-assessments help you to assess yourself before the actual exam day. Therefore, with proper Qbank usually combined with a preferable concise medical review such as the Toronto Note and so on, one should be able to ace the MCCQE1 with a high score.
4- Apply For Medical Residency In Canada
In Canada, you will apply for residency positions through the Canadian Resident Matching Service (CaRMS), which is an electronic service or, better put, an online application where you will be given a timeline to upload all requested documents, select a medical program in which you are interested, and a province where you will practice as a physician, and then the system will send your application to the program of your choice. If you match, you will be contacted for an interview. Preparation for an interview is critical, so review some residency interview tips and conduct research on particular programs before the interview.
5- Complete Your Residency
After passing the MCCQE1 exam and becoming a licensed doctor, you must still complete a residency program before you can practice as an independent doctor according to the MCC rules. It allows you to get trained and adapt to real-life issues of your medical career under the mentorship of senior doctors at the beginning of your career. The term of residency differs based on chosen medical specialty. For a general physician, the residency term is two years, but it may be up to 6 years for specialists. If you choose to go for a sub-specialty, you may also have to add another 2 to 3 years in residency.
To become a doctor in Canada, you have to study hard and give your best efforts for at least ten years in this entire process, in both studies and residency. Especially passing the MCCQE1 exam requires a lot of dedication, persistence, and smart utilization of resources. By doing that, you can become a doctor in Canada and live a respectful life of helping others and having a great career.
6- Physician Return Of Service (ROS) Programs:
In return for residency training, doctors in the Physician Return of Service (ROS) program agree to practice in a qualifying community for up to five years. ROS program, in general, assists in ensuring a stable physician supply, expanding physician distribution to provide better care for Canadians, and improving access to doctors across Canada, especially in places where physician supply is low.
The Alternative Path To Becoming A Doctor In Canada:
The alternative pathway of becoming a Canadian doctor/ physician is challenging, and it does require you to pass the NAC exam. This path has several steps that must be followed, such as registering in the system passing the MCCQE1 Exam and NAC exam, which is much easier compared to the past, where the MCCQE2 was also part of a requirement for certain provinces in Canada. The good news is due to COVID-19, the MCCQE2 was first suspended and then permanently eliminated from International Medical Graduates (IMGs). An alternative path, IMGs with clinical experience have more possibilities than those who just graduated from foreign medical school. Let’s have a closer look at the alternative pathway of becoming a doctor in Canada and see those possibilities after going through some basic terminology and essential information below.
Most Common Questions about becoming a doctor in Canada
– Who is called International Medical Graduates or IMGs?
International Medical Graduates or IMGs are a candidate who has either graduated from medical school abroad or completed postgraduate residency training outside of Canada.
– What are resources available for International Medical Graduates in Canada?
There are several resources available to help IMGs with this transition, such as Health Force Ontario, Canadian Resident Matching Service (CaRMS), and last but not least elective and observership programs.
The Health Force Ontario Access Centre provides information, guidance, and advice about the medical licensing process and alternative career options in health care. CaRMS, on the other hand, works closely with the medical education community to match applicants to postgraduate medical training programs in Canada through four residency matches each year. However, the best is to explore the online resources provided on the CaRMS website to find out what you need as an international medical graduate before applying for CaRMS.
– What is the NAC exam?
NAC stands for National Assessment Collaboration. The NAC exam is a major difference between two common and alternative paths to practice medicine in Canada. NAC exam is an oral examination consisting of a series of stations, each of which assesses a different area of medical expertise by introducing a clinical problem and outlines the candidate’s tasks such as taking a medical history or performing a thorough physical examination to evaluate International Medical Graduates or IMGs.
– What is the Licentiate of the Medical Council of Canada (LMCC)?
The Licentiate of the Medical Council of Canada (LMCC) is a part of the Canadian Standard for independent practice, the set of requirements such as passing the MCCQE1 exam for an award of a full unrestricted license to practice in Canada. The Medical Council of Canada (MCC) grants the LMCC to doctors.
For International Medical Graduates or IMGs, the story is slightly different. IMGs come from medical schools all over the world. Every individual’s narrative reflects a wide spectrum of experience, ranging from years of practice to no patient encounter at all. Because medical education differs greatly among IMGs, all IMGs must take a set of standardized examinations such as the NAC exam prior to gaining entrance to residency in Canada to verify they fulfill the minimal Canadian medical education standards and have the necessary skills to begin residency training in Canada. Although, those IMGs whoprovincial or territorial medical regulatory authority have completed postgraduate residency training outside of Canada in an approved jurisdiction can apply for the Ready to Practice is a program.
– What is a Ready-To-Practice program?
Ready to practice is a program for those International Medical Graduates or IMGs who have completed postgraduate residency training outside of Canada in an approved jurisdiction and plan to practice in Canada. They can apply for a practice-ready assessment through a participating licensing authority. The downside of this program is that not all provinces participate; however, to apply for a practice-ready assessment, please contact the provincial or territorial medical regulatory authority where you currently reside in Canada.
– What Is The MCCQE1 Exam?
The Medical Council of Canada Qualification (MCCQE1) exam part 1 is the first and one the most challenging step toward becoming a licensed doctor in Canada. The MCCQE1 exam is a computer-based one-day exam. In the morning session, you have up to four hours to complete 210 Multiple-Choice Questions. The Clinical Decision-Making component consists of 38 cases with short-menu and short-answer write-in questions. Proper preparation is essential for success on the MCCQE1 exam, and you should make every effort to earn the maximum possible score on the MCCQE1 exam. If you have plans to study for the exam and need help to pass the MCCQE1 exam on the first attempt, look no further than Ace Question bank.
Ace Question bank has created all in one online reference to provide a comprehensive guide and help both Canadian and International Medical Graduates in preparing for the MCCQE1 exam. Knowing the quality of health care provided in Canada, Ace Qbank, instead of offering a wide range of options for the MCCQE1 preparation, has focused on providing the most MCCQE1 exam-relevant information to ease the burden of the MCCQE1 preparation. Ace Qbank developed a comprehensive question bank for the MCCQE1 preparation with the most updated and evidence-based medicine content available in each of the major clinical disciplines: obstetrics/gynecology, pediatrics, medicine, emergency medicine, surgery, and psychiatry that leads to the highest possible score on the MCCQE1 exam.
Currently, offering over 2000 high-yield, MCCQE1 exam-style questions with in-depth explanations helps you prepare for the first part of the MCCQE1 exam. Over 100 top-notch clinical cases are designed to help you prepare for the Clinical decision-making (CDM) section of the MCCQE1 exam. In order to reinforce your knowledge of challenging objectives of MCCQE1 Ace Qbank using summary points, tables, flow charts, and in-depth text explanations for wrong answers. That allows you to apply these concepts by practicing clinical vignettes and becoming familiar with actual MCCQE1 exam situations. Once you feel ready, you can put to the test your clinical knowledge and test-taking strategy before actual MCCQE1 with self-assessment to ensure success in your MCCQE1 exam.
Try Free Demo Of The Best Question Bank In Canada
The Process Of Becoming A Doctor In Canada:
1- Check Eligibility:
Canadian citizens and permanent residents with medical degrees from schools not accredited by any committee in Canada are eligible to apply for a residency position.
2- Registration:
First, you need to open an account in physiciansapply.ca, then go to application and eligibility to verify that your school of medicine meets the requirements through your physiciansapply.ca account, and after your medical school is eligible, you’ll be required to provide an official identity along with other required documents. It is imperative to know that you can only apply if your medical degree/diploma is currently being verified or has been successfully verified; otherwise, you have to verify your medical diploma first.
3- Pass The MCCQE1 exams
The MCCQE1 exam is one of the requirements of becoming a licensed medical professional in Canada. You need to pass the MCCQE Part 1 exam. This exam is to assess your medical knowledge, competency, and clinical decision-making skills before you are allowed to work as an independent doctor/physician in Canada.
4- Apply For Medical Residency In Canada:
In Canada, you will apply for residency positions through the Canadian Resident Matching Service (CaRMS), which is an electronic service or, better put, an online application where you will be given a timeline to upload all requested documents, select a medical program in which you are interested, and a province where you will practice as a physician, and then the system will send your application to the program of your choice. If you match, you will be contacted for an interview. Preparation for an interview is critical, so review some residency interview tips and conduct research on particular programs before the interview.
However, those IMGs who have advanced medical training and years of experience can also apply for the Ready-To-Practice program after passing the MCCQE1 and NAC exams.
5- Complete Your Residency
After passing the MCCQE1 exam and becoming a licensed doctor/ physician, you must still complete a residency program before you can practice as an independent doctor according to the MCC rules. It allows you to get trained and adapt to real-life issues of your medical career under the mentorship of senior doctors at the beginning of your career. The term of residency differs based on your specialty. For a general physician, the residency term is two years, but it may be up to 6 years for specialists. If you choose to go for a sub-specialty, you may also have to add another 2 to 3 years in residency.
6- Physician Return Of Service (ROS) Programs:
IMGs also enter the Physician Return of Service (ROS) program to practice in a qualifying community for up to five years. ROS program, as mentioned above, assist in ensuring a stable physician supply, expanding physician distribution to provide better care for Canadians, and improving access to physicians across Canada, especially in places where physician supply is low.
Need Help With Your MCCQE1 Exam Preparation?
Proper preparation is essential for success on the MCCQE1 Exam, and you should make every effort to earn the maximum possible score on the MCCQE1 Exam. If you’re having trouble keeping to your study plan or if certain objectives are challenging for you, get the help you need to pass the MCCQE1 Exam on the first attempt.
Ace Qbank has got your back with over 2000+ high yield questions, many Clinical Decision-Making (CDM) cases, and several self-assessments available to challenge and push you to your limit.
To facilitate preparation for the MCCQE1 Exam, we developed the Ace Qbank based on the Medical Council of Canada (MCC) objectives. Our team reviews the question bank regularly based on current guidelines and recommendations, and we implement any changes we make as soon as possible to enhance your learning experience. Our objective is to keep the information up to date and in compliance with medical standards of care to avoid surprises during the test. At Ace Qbank, we’ve got you covered.
We invite you to sign up for the Ace Qbank demo today and see the difference our elite question bank makes!